Some molds are beneficial, others are dangerous, and some are both. Learn about Penicillium mold, its many helpful abilities plus its dangers.
What to Know About Penicillium Mold

On This Page
What Is Penicillium Mold?
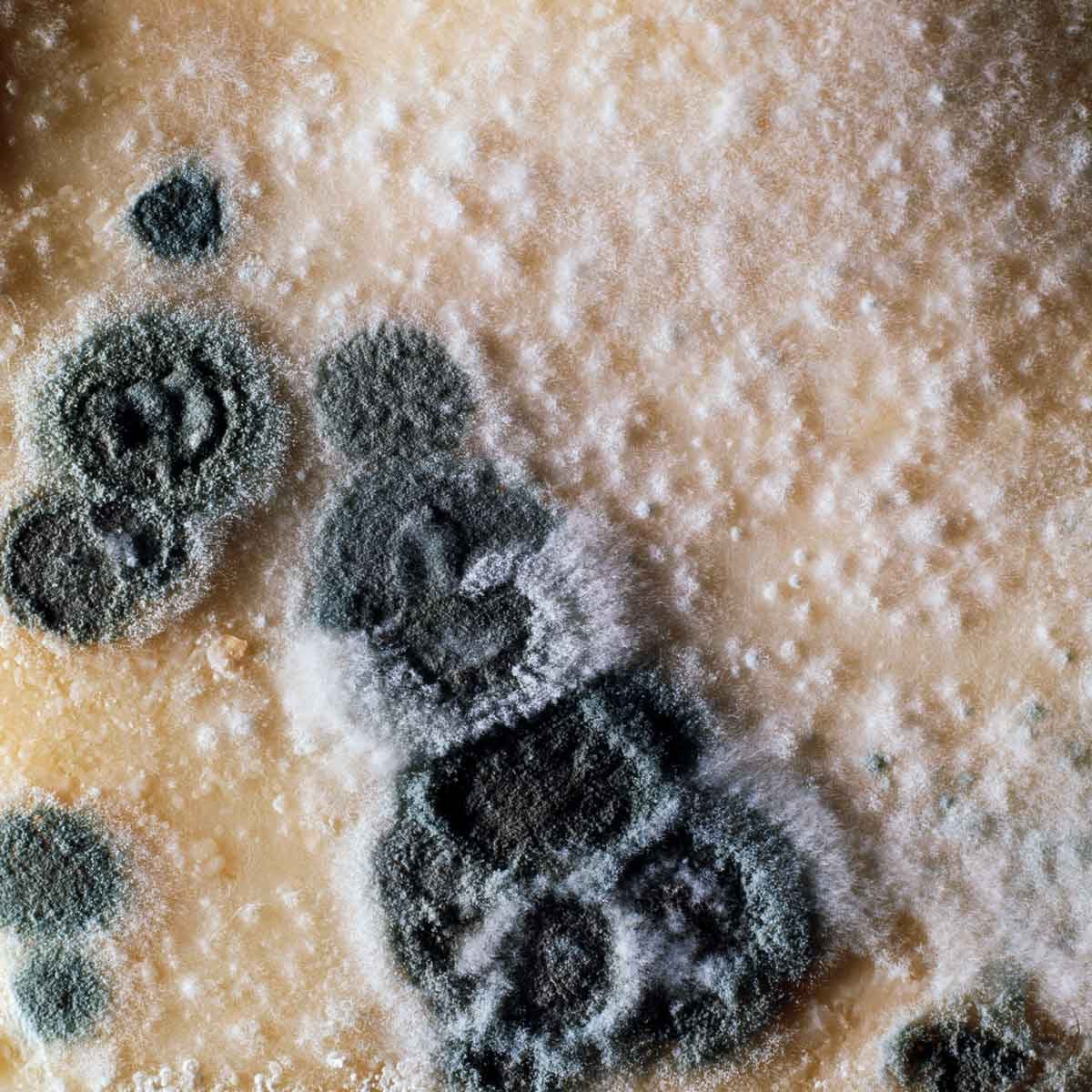
This family of molds was first identified in 1809 in a book by German naturalist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. Most of the estimated 300 or more species produce blue, green or yellow spores, and are one of the most common causes of fruit and vegetable spoilage. Spores are mostly spread in the air, and grow best in cool or moderate climates and damp environments. Some species of Penicillium are extremely useful in the production of certain meats, cheeses and antibiotics like Penicillin, which comes from Penicillium chrysogenum.
Where Is Penicillium Mold Commonly Found?
Penicillium is found all over the world in cool, damp environments. It grows most often on decaying organic materials such as fruits, vegetables and vegetation. Old bread, spoiling apples and pears, and rotting plant bulbs are all perfect habitats for various Penicillium species, which often show up as blue or green fuzzy growths. Aspergillius penicillium is the strand Sacenti sees most often. “It’s usually found on lumber, building materials, plywood and joists in the basement,” he says.
What Are the Health Effects of Penicillium Mold?
“It’s not extremely dangerous, but everyone’s respiratory system is different,” Sacenti says, “So it may bother you more than it bothers someone else.” Like many molds, Penicillium can threaten those with weak or compromised immune systems, causing allergic reactions or infections. Some species produce mycotoxins which are known carcinogens. Others species cause measurable organ damage when inhaled. When ingested, one species, called Penicillium marneffei, can cause serious infections that affect the lungs, kidneys, spleen, liver and bone marrow.
How to Remove and Prevent Penicillium Mold
Like most molds, Penicillium can only grow where there’s sufficient moisture. Some molds grow best in homes with high relative humidity, which is easy to fix: Open windows or install a heat recovery ventilator (HRV) in a cool climate, or run your air conditioning in hot regions. Sacenti also suggests running a dehumidifier in your basement.
Pencillium has relatively low moisture needs, sometimes growing in homes with normal airborne humidity as long as there’s at least one moist surface somewhere. To prevent Penicillium spreading, make sure your home is dry and well ventilated. Don’t keep spoiling food of any sort, because it’s a perfect environment for spores to take root.
If you find a small amount of mold, soak it thoroughly with a non-toxic registered fungicide. For infestations larger than about 36 x 36 inches, call mold specialists.
About the Expert
- Michael Sacenti owns American Healthy Homes. He has 10 years of experience in the mold remediation industry and 40 years experience in real estate maintenance.



















